
Brewer's Sparrow
| Scientific Name | Spizella breweri |
|---|---|
| General Description | L 5.5”, WS 7.5”, 0.37 oz. Gray-brown overall, unstreaked breast, white eye ring, and small bill. |
| Status | Occurs in North Dakota from May to mid-September. Breeding season mid-May to late July. |
| Abundance | Uncommon. |
| Primary Habitat | Big sagebrush patches within shortgrass prairie. |
| Federal Status | Migratory Bird. |
| Reason for Designation | A sagebrush obligate species, Brewer’s Sparrow is showing a survey-wide decline. It is included on the National USFWS Birds of Conservation Concern list and BCR 17. Partners in Flight (PIF) identifies the Brewer’s Sparrow as a Regional Concern Species and a Common Bird in Steep Decline. It is a peripheral species in North Dakota. |
Locations and Conditions of Key Habitat
Preferred Habitat
A sagebrush obligate, Brewer’s Sparrow is closely associated with shrub communities dominated by big sagebrush. Sagebrush grasslands with >10% average shrub cover and average shrub height of 0.5-1.5 m are preferred. Not present in areas where shrub cover decreases below 3-8% average. May also occasionally occur in juniper woodlands. The nest is located in sagebrush or other shrubs. Prefer nesting in medium-sized, alive or mostly alive shrubs of 50-90 cm tall with the nest located from 7-104 cm off the ground. Forage in tall, live shrubs or on ground for alfalfa weevils, aphids, caterpillars, beetles, or seeds.
Key Areas and Conditions for Brewer's Sparrow in North Dakota
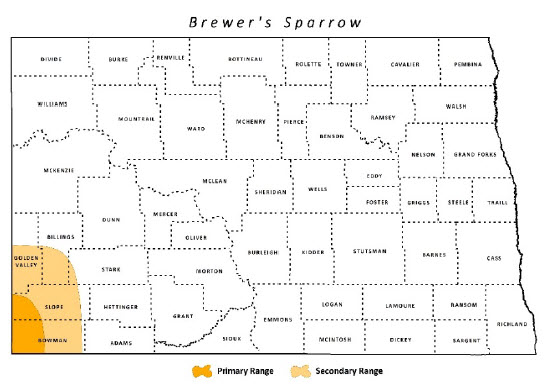
No specific sites have been identified, but the species is likely to occur only in western Slope and Bowman counties.
Problems Which May Affect this Species
Habitat
Loss and/or degradation of big sagebrush habitat. Fire can destroy sagebrush and can take many years for the community to recover. Invasion of non-native grass or forb species (e.g. clubmoss) could negatively affect the sagebrush community.
Other Natural or Manmade Factors
Uncommon host of brown-headed cowbirds. No information available on the effect of pesticides. Brewer’s Sparrow abundance decreased significantly with increasing well density/km² in Wyoming (Gilbert and Chalfoun 2011).
Research and Survey Efforts
Current Research or Surveys
- There is currently nothing specific to the species in North Dakota.
Previous Research or Surveys
- Research into sagebrush steppe habitats and associated bird species on the edge of the sagebrush ecosystem was completed in 2004. The study characterized the vegetation and avian associations in the transitional zones of North and South Dakota. A total of 15 Brewer’s Sparrows were counted in North Dakota during two summers of field work, or were recorded in 7.4% of the sites surveyed. They were detected on sites with a higher percentage of sagebrush cover and shrub density (Lewis 2004).
- Little effort has been applied to research or surveys specifically for Brewer’s Sparrow in North Dakota.
- Numerous published reports and gray literature on this species throughout its range.
Additional Research or Surveys Needed
Periodic monitoring to gather vegetation and land use trends in the sagebrush transition zone may be needed to identify threats and prevent loss of habitat.
Population and Trend Estimates
- PIF Global Population Estimate: 13,000,000
- PIF North American Population Estimate: 13,000,000
- PIF North Dakota Population Estimate: unknown, less than 1,000
- North Dakota BBS Trend: data insufficient
- Survey-wide BBS Trend 1966-2012: -0.95
Management Recommendations
- Identify and protect remaining intact sagebrush habitats.
- Maintain sagebrush communities.
- Avoid complete removal of sagebrush, but extremely dense sagebrush stands (>50%) may need to be thinned.
- Avoid burning, as historically sagebrush (a slow regenerator) burned only every 60-100 years.
- Avoid pesticide use in sagebrush habitats, or delay spraying until September.
Monitoring Plans
According to the Partners in Flight Landbird Conservation Plan, long-term population trend monitoring such as the Breeding Bird Survey is generally considered adequate, but may not account for some issues (e.g. bias). However, few BBS routes in North Dakota intersect with Brewer’s Sparrow range. Future monitoring proposals should follow recommendations North American Bird Conservation Initiative ‘Opportunities for Improving Avian Monitoring’.
2005-2015 Progress
The Brewer’s Sparrow remains a Level III Species of Conservation Priority.
Note: A listing of works consulted when compiling the information on this page may be found in the 2015 State Wildlife Action Plan.

