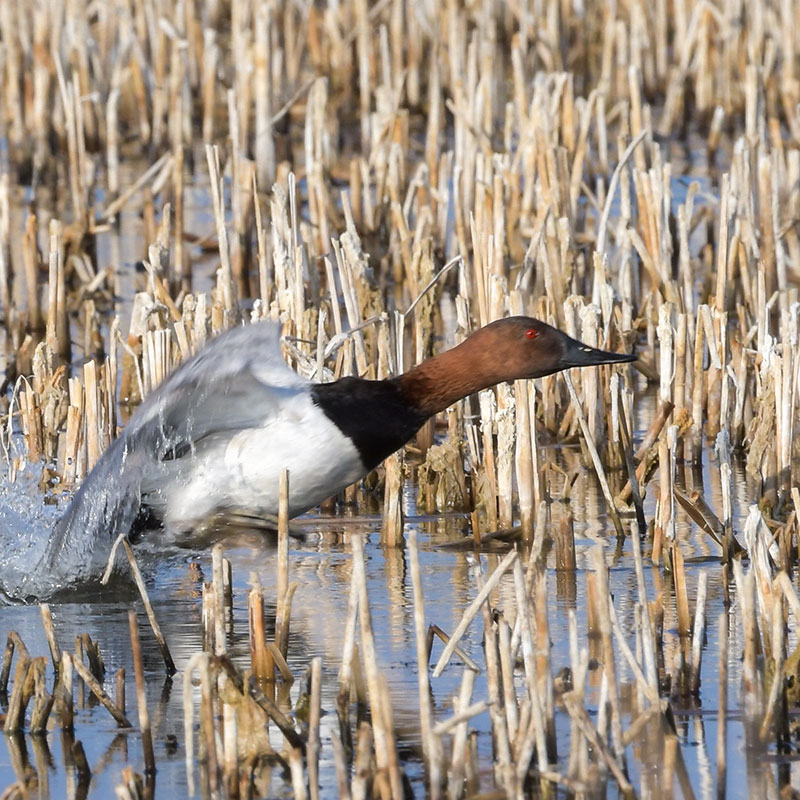
Canvasback

NDGF
L 21”, WS 29”, 2.7 lb. Long, pointed, black bill on a sloping, dark red head (male), red eye, gray and white pattern on back and sides.
Status in North Dakota
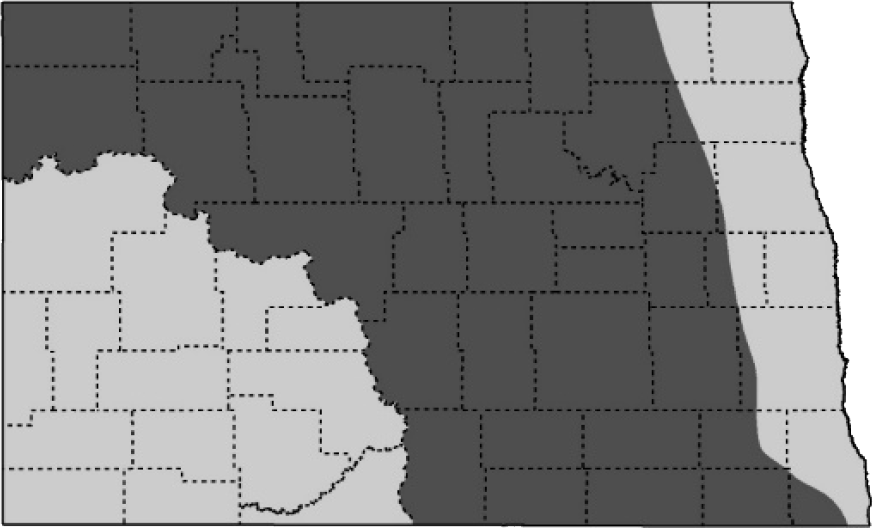
ccurs in North Dakota from mid-March to mid-December. Peak breeding season from mid-May to mid-August.
Reason for SWAP Designation
At-risk, ND range important (SGCN b.).
ND ranks 1st out of 14 states for highest percent of the global population (18.03%) during the breeding season (eBird).
ND has high stewardship responsibility for this species.
Threats
Loss and degradation of wetlands, drainage and wetland consolidation.
Hydrologic shifts in wetlands of the PPR due to wetland consolidation and drainage, climate and land use changes (i.e. lakeification).
Increasing applications of agrochemicals and impacts to water quality, the wetland vegetative community, and the aquatic invertebrate community.
More frequent or intense harmful algal blooms.
Aquatic nuisance species spreading and damaging wetland ecosystems.
Human disturbance, such as by recreational boaters, at staging and stopover sites.
Collisions with human-made structures (e.g. overhead lines, wind turbines).
Research and Monitoring
Habitat requirements and demographics have been extensively researched on the breeding grounds.
The Waterfowl Breeding Population and Habitat Survey (May Survey) is a long-standing survey conducted in the U.S. and Canada and provides annual breeding population estimates for most ducks in North America.
The NDGF has also conducted an annual spring breeding duck survey since 1948.
Management Recommendations
- Preserve and conserve semi-permanent wetlands and wetland complexes.
- Restore hydrology and vegetation to degraded wetlands.
- Leave or plant grassed buffer strips around wetlands and waterways to prevent erosion and runoff into wetlands.
- Conduct management to open cattail-choked wetlands.
- Stocking fish in shallow wetlands can be detrimental to waterfowl production.
- Conscientious and appropriate application of agrochemicals.
- Follow aquatic nuisance species rules and regulations.
- Follow beneficial or best practices during the design, siting, construction, operation, and maintenance of tall structures (e.g. transmission lines, communication towers, wind turbines).