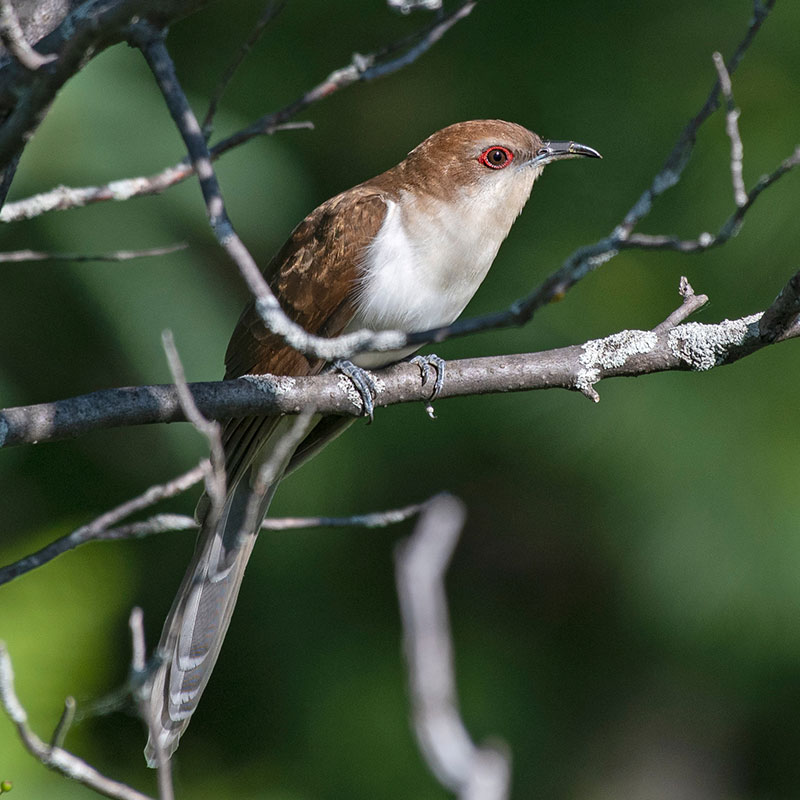
Black-billed Cuckoo

Adobe Stock
L 12”, WS 17.5”, 1.8 oz. Slender, long-tailed, brown upperside, and off-white underneath. The black bill and red eye ring distinguish it from the yellow-billed cuckoo.
Status in North Dakota
Occurs in North Dakota from mid-May to late-September. Peak breeding season mid-June to late July.
Reason for SWAP Designation
At-risk based on recent regional assessments (SGCN c.).
ND ranks 7th out of 26 states for highest percent of the global population (1.26%) during the breeding season (eBird).
The Black-billed Cuckoo is declining, and the population decreased 68% since 1970.
Threats
Loss and degradation of native riparian habitat.
Development in wooded areas along major rivers may reduce cuckoo nesting habitat.
Overgrazing of woody draws and other woodlands affects the vegetative structure and composition.
Black-billed Cuckoos rely heavily on caterpillars for food and can be especially gregarious during caterpillar outbreaks.
Pesticide use may reduce prey availability.
Classified as climate-threatened, Black-billed Cuckoo is projected to lose more than half of its current distribution by 2080, with potential net gains of new areas (Audubon).
Some mortality from collisions with structures and communication towers, probably in part due to nocturnal migration behavior.
Research and Monitoring
Habitat requirements are generally known.
Little is known about reproductive success, annual adult survival, or fledgling survival.
Additional information is needed on migration and wintering behaviors.
The Breeding Bird Survey, eBird and Partners in Flight Databases are key sources of information on distribution and population trends.
Monitoring could involve targeted call-response surveys.
Management Recommendations
- Protect and restore native riparian habitats.
- Limit or exclude grazing in riparian areas.
- Choose pesticides with the lowest toxicity to non-target organisms, or use biological insecticides such as B.t.
- Prune tent caterpillar masses from trees.
- Follow beneficial or best practices during the design, siting, construction, operation, and maintenance of tall structures (e.g. transmission lines, communication towers, wind turbines).